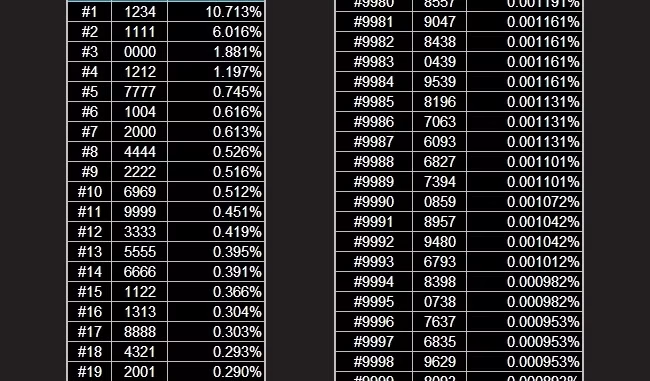
Your bank PIN is one of the most important layers of protection for your finances but unfortunately, many people unknowingly choose combinations that are shockingly easy to guess. While it may feel convenient to use something simple, using the wrong numbers could make you an easy target for fraud or theft.
Never use obvious sequences like “1234” or “0000.” These are the most commonly guessed PINs because people assume no one would try something so basic yet these are the first combinations a thief will try if they get access to your card.
Also, avoid using your birth year, birthdate, or parts of your phone number. While these are easier to remember, they are often the first details someone could figure out from your ID, social media, or stolen wallet.
PINs like “2580” (which is a straight vertical line on the keypad) or “1111” (same digit repeated) are also high-risk.
These patterns may look random to you, but they’re predictable to someone trying to guess.
A strong PIN should be a mix of unrelated numbers not tied to your personal life and not following an obvious pattern.
Your money deserves better security, and that starts with smarter choices
Leave a Reply